Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a constellation of debilitating conditions that result in inflammation of the digestive tract. These inflammations are then involved in an assemblage of symptoms that cause a big burden in a person’s daily life. There exist two types of inflammatory bowel diseases, and they are Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. And even though both syndromes were probably caused by inflammation of the gut they do have some features which set them apart.
Read our Full Articles about Crohn’s Disease: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing This Chronic Condition
also Read our Full Articles about Ulcerative Colitis Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
This article is targeted to highlight these distinctions by comparing and contrasting Crohn’s disease and Colitis ulcerative. We can discover such hidden patterns of the disease offering valuable symptoms, causes, and treatment approaches by identifying the distinguishing characteristics of diverse conditions. The information will also transform the patients and their families by equipping and enlightening them to be able to easily handle an IBD diagnosis and explore helpful management methods.
Similarities and Differences
This part of the same article delves deeper into how Crohn’s-like UC (Ulcerative Colitis) can both overlap and diverge. Here’s what it will explore: Here’s what it will explore:
Similarities
Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases:
The conditions are both chronic having long-term effects on gut discrepancy and inflammation.
Similar Symptoms During Flare-Ups:
Both can be associated with symptom aggravation (a flare-up) followed by a stomachache, diarrhea, and urgent bathroom pushing.
No Cure, But Manageable:
Regrettably, no curative treatment is available for either, but the symptoms can be managed through a remission treatment (the periods when the symptoms are at their minimum or virtually absent).
Impact on Quality of Life:
These situations may affect the health of an individual in different ways, but they may all change the life and quality of life of the person.
Differences
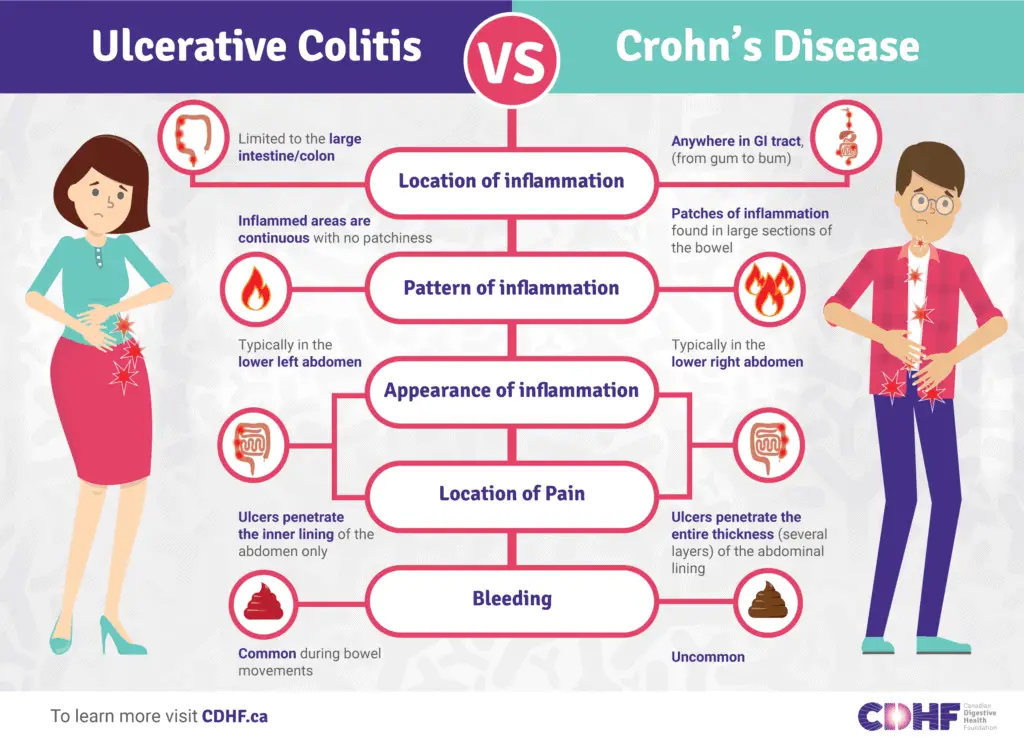
Location and Pattern of Inflammation: Location and Pattern of Inflammation:
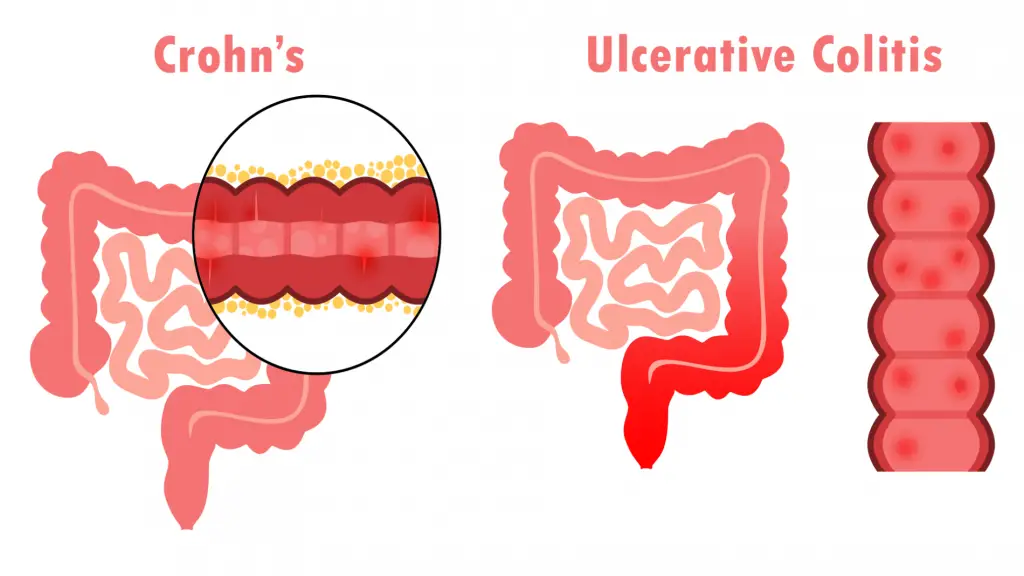
Crohn’s: Inflammation can involve any part of the digestive tract (pan-local and separated lesions).
Ulcerative Colitis:
Untouched as far as the small intestine is concerned, and limited only to the inner lining of the colon and rectum. However, the inflammation continues to spread proximally, upwards from the rectum towards the colon.
Presence of Granulomas:
Immune cell collection, which is microscopic in dimension, has been earlier observed in Crohn’s disease tissues.
Type of Bowel Movement:
Crohn’s: Can be chalky or fatty since fat absorption is hindered.
Ulcerative Colitis: Stools usually are red with discomfort being caused by a damaged mucous membrane surface
Conclusion
Finally, the essay concludes by highlighting the main findings and pointing out the necessity of consulting an equalized provider. Here’s a breakdown of what it will cover: Here’s a breakdown of what it will cover:
Recap the Key Differences:
Finally, highlighting key features that are different for Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, the main points would conclude. You may talk about the inflamed places, granuloma presence, and the types of bowel movements to spot respective patients of this condition.
Emphasize the Importance of Professional Medical Advice:
This piece is just an overview; however, I surely affirm that doing anything requires consulting a healthcare professional. They can perform the necessary tests and draft an optimal management plan for every unique patient. If positive, the development impact can be substantial as educational attainment is a critical factor in determining an individual’s economic status. In many countries, individuals with higher levels of education obtain better-paying jobs and are more likely to secure employment in the formal sector.