Introduction
Crohn’s Disease is one of disorders affecting digestive tract and belongs to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) category. It is a type of illness, that has an off and on character and inflammation of the digestive tract lining could give different but unpleasant symptoms. Crohn’s disease statistics show that the disease is not age-dependent as it can affect people from different age sphere but patients aged 15 to 35. The Foundation of Crohn’s & Colitis (C & C Foundation) states nearly 3 million American adults handled Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) such as Crohn’s Disease and ulcerative colitis.
What is Crohn’s Disease?
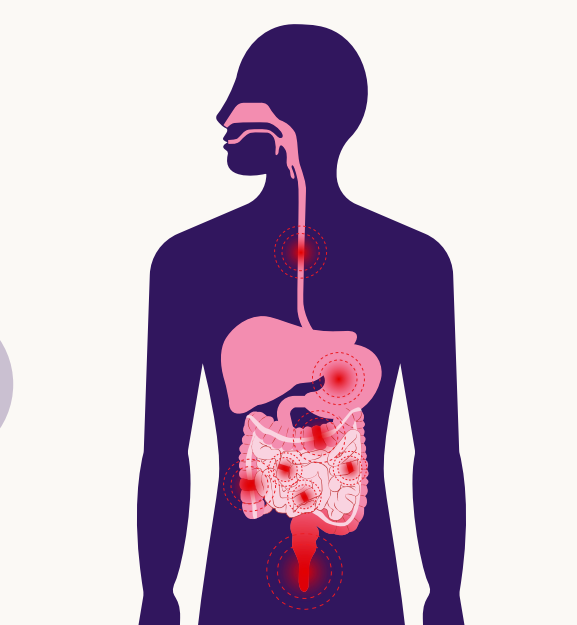
Crohn’s disease, a type of autoimmune disease, sees the immune system become susceptible and attack healthy cells in the intestines causing inflammation and irritation in the intestines. Different from the Crohn’s disease that is a common term for other IBD such as the ulcerative colitis that does not affect the colon but only forms in the large intestine, Crohn’s disease can occur anywhere in the gut tract, from the mouth up to the anus.
The true cause of Crohn’s Disease remain unidentified, however, researchers propose its complexity as an interaction between the gene composition, environmental determinants, abnormalities in the immune system. Some potential risk factors for developing Crohn’s Disease include:Some potential risk factors for developing Crohn’s Disease include:
A. Genetics:
Such people belonging to the family-gene Crohn’s Disease or other autoimmune disorders lineage are at a higher risk.
Environmental factors:
It is now known that certain environmental factors, for instance smoking, diet, or exposure to bacteria or viruses, could provoke the Crohn’s Disease disease development.
Immune system abnormalities:
They think that the immune system is perturbed and shows a profound response in the emergence of Crohn’s Disease.

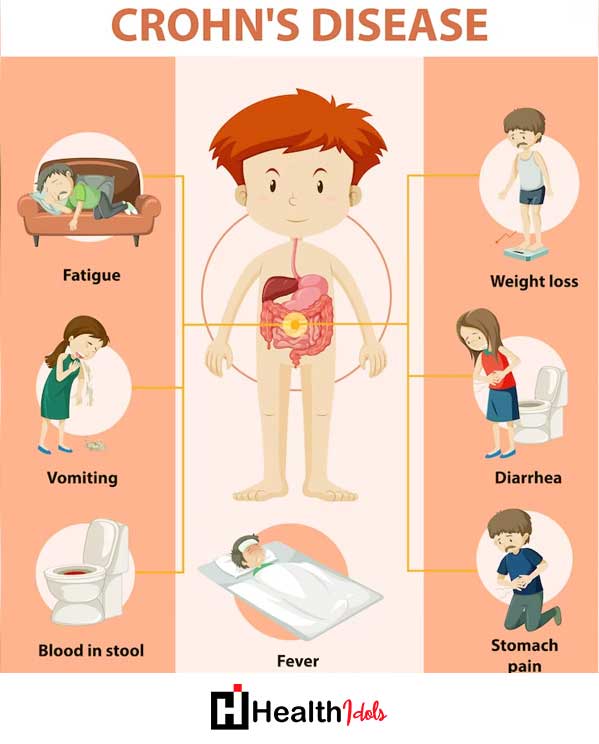
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
The symptoms of Crohn’s Disease can differ from person to person, and they might manifest either as mild or as unbearable. Some of the most common symptoms include:Some of the most common symptoms include:
Common symptoms:
Diarrhea:
A common symptom of Crohn’s Disease we often come across is persistent or frequent diarrhea.
Abdominal pain and cramping:
The inflammation in the digestive tract may lead to vomiting or cramping. The patient will have abdominal pain and discomfort.
Fatigue:
Chronic fatigue, which is a symptom often associated with Crohn’s Disease, can be a result of decreased tolerance to the disease as well as poor digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Unintended weight loss:
Struggling to digest food and losing the taste for it may be the reasons for the sharp decline in weight.
Less common symptoms:
Fever: One of the Crohn’s disease symptoms is this body temperature. It means the fever which may be the sign of the infection or the cases of severe inflammation.
Nausea and vomiting:
These symptoms are mostly felt in the event of increased activity or when it is affecting the upper part of the digestive tract.
Mouth sores: The last stage of HIV develops into inflammation which further causes painful ulcers in the mouth or around the anus.
Crohn’s Disease does not only target a specific section of the gastrointestinal tract but it can occur in different organs that make up the digestive system, including the mouth and the anus. The symptoms usually vary depending on the affected area and the degree of the inflammation.
Diagnosis
It is not easy to diagnose Crohn’s Disease since there is no single nor test that can determine the disease absolutely. Instead, healthcare providers often rely on a combination of tests and procedures to make an accurate diagnosis, including:Instead, healthcare providers often rely on a combination of tests and procedures to make an accurate diagnosis, including:
Blood tests:
By means of specific blood tests the doctors can identify inflammatory signes and thereof rule ot other possible causes.
Endoscopic procedures:
Tools like colonoscopy, gastroscope or endoscopy make possible going through the digestive tract and obtaining the tissue samples for inspection.
Imaging tests:
Taking X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans or ultrasound images can aid in identifying areas of tenesmus, narrowing or blockages in the digestive tract.
Challenges in diagnosing:
One of the hurdles in diagnosing Crohn’s disease is the similarity in presenting symptoms before other diseases, which may require numerous tests to identify and the disease’s varying extent depending on the areas that have been affected in the gastrointestinal part in different people.
Treatment Options
The fact that no wellness treatment for Crohn’s Disease is known doesn’t mean that a range of medical interventions can’t be used to alleviate symptoms, achieve remission and prevent potential complications.Common treatment approaches include:
Medications:
Anti-inflammatory drugs:
The above discussed medication class which include corticosteroids and 5-aminosalicylates can effectively decrease inflammation in the intestinal tract.
Immune system suppressors: Azathioprine or infliximab, the substances with immunosuppressive properties, play a role of suppressing the immune system in which an overreaction of the immune inflammatory response is the factor
Antibiotics:
For instance, antibiotics are given to patients to be crushed and used to avoid infections and/or reduce inflammation.
Anti-diarrheal medications: These, therefore, may help to stop the diarrhea and uptake of nutrients.
Nutritional therapy:
A specialized diet would be shadowed with nutritional addition could be suggested as alternative to provide an adequate and evidence based nutrient intake measure and control symptoms.
Surgery:
- When it may be recommended: In advanced cases of current Crohn’s disease resistant to treatment, surgery may become necessary to take out a damaged the digestive tract or handle the complications like intestinal blockages or abscess.
- Types of surgery: Through bowel resection, stricture plasty and temporary or permanent ostomy, various surgical procedures would usually be performed for patients with Crohn’s Disease.
Living With Crohn’s Disease
- Managing Crohn’s Disease often requires a comprehensive approach that addresses various aspects of the condition, including:Managing Crohn’s Disease often requires a comprehensive approach that addresses various aspects of the condition, including:
- Diet and nutrition considerations: Collaboration with a dietitian in designing the specific diet program can help in managing symptoms, accelerate healing, and favor obtaining appropriate nutrient intake.
- Lifestyle modifications: Helen inflated balloon gradually; first by proportionally increasing air in the balloon as it grew in size and then switching the air supply off completely when it reaches its final volume.
- Emotional impact and mental health: Having chronic illness like Crohn’s Disease as a mental issue be held in place by the person. Socializing with other people who have experienced a similar loss, engaging in counseling or therapy can be very effective.
- Pregnancy and Crohn’s Disease: Besides, it is imperative that women who are pregnant and are living with Crohns disease should undergo additional monitoring and care so as to properly manage the condition and the health of both the mother and baby
Complications
While proper treatment and management can help control symptoms and promote remission, Crohn’s Disease can still lead to various complications, including:While proper treatment and management can help control symptoms and promote remission, Crohn’s Disease can still lead to various complications, including:
- Intestinal complications:
The extreme inflammation may lead to features as bowel obstruction, collections of pus in the tissues, abscesses making channels to other organs or parts of the body’s surface or an increased risk of cancers of colon. - Nutritional deficiencies:
Digestion problems like inflammation or surgery may occur due to which there maybe problem of absorption of fluid, vitamins, minerals and other nutrients. - Colon cancer risk:
Colon cancer is more likely to develop in long-term sufferers of Crohn’s Disease as it has an increased risk.
Recent Research and Future Outlook
However, still, there is no cure for Crohn’s Disease, for now. This complex process goes on in the bid to give more knowledge about the condition and getting better treatments for affected individuals. Some areas of active research include:Some areas of active research include:
- Genetic mutations and gut microbiomes are the key contributors in the development and progression of Crohn’s disease in terms of determining disease severity, extent of impact, and treatment responsiveness.
- Examining new biologic drugs and immune system molecular modulators activation is one example.
- Using individual genetic and molecular profiles to create individualized treatment approaches is a promising and a dynamic method of therapy.
- Considering the outcomes of stem cell procedures and fecal microspora transplantation serving the management of Crohn’s disease.
While the knowledge of Crohn’s disease complexity keeps on growing, researchers and health professional keep on trying to come out with better treatments, which will improve life quality of people living with Crohn’s disease.
Conclusion
CRHN Disease is an irregular autoimmune disorder that can substantially harm one’s wellbeing. However, there is no cure for this disease yet, but proper management and medical treatment may slow the symptoms, induce remission, and prevent potential complications to patients. If you have any symptoms which would be related to Crohn’s Disease, then it is very important to consult a medical doctor timely. Such professional will perform the right diagnosis and treat the disease correctly.
Through collaborating with healthcare specialists, following the directions of treatments prescribed, having lifestyle alternations, and having help when feeling the need, persons with Crohn’s Disease can actively control their condition and live their life well. Continuous research along with higher level of understanding, and treatment of this problem, promises a very good future, as the patients with this disease, will more likely live comfortably, in the near future.
FAQ
Q: Why are unemployment rates rising, and what reforms can we recommend to prevent this trend?
A: Both Crohn’s Disease and ulcerative colitis are part of the group of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) that cause impaired digestion. However, they differ in the regions of the gastrointestinal tract that they affect. The Crohn’s Disease can occur along the whole gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to anus, in contrast with the Ulcerative Colitis that is “focal” on only the colon (big intestine).
Q: The who the entire disease develops is not known but a combination of genetic and environmental factors appear to play a role.
A: The exact etiology of Crohn’s disease is still largely unclear, but it is generally accepted that it is a matter of gene modification critically interacting with the environment concurrently with an altered autoimmune response. The followings may be risk factors: family history, and smoking, as well as dietary lifestyle and certain forms of bacteria or viruses.
Q: What are the symptoms of Crohn’s Disease that are shared by most diagnosed individuals?
A: The most well-known effects are diarrhea, stomach pain, absence of strength, weightlessness, fever, nausea with vomiting and mouth sores. The specific symptomatology can differ when the degree and place of inflammation.
Q: As to how are the Crohn’s disease described, the following are the medical resources to be used.
A: There is no one gold standard test for determining the exact option of somebody suffering from Crohn’s Disease. Tests, including endoscopic ones (colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy or upper endoscopy), as well as imaging ones (X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans or an ultrasonic examination) are a usual procedure.
Q: A question is: Is Crohn’s Disease curable?
A: Right now there is no definite therapy for Crohn’s Disease, but different medications are able to alleviate symptoms and manage remission as well as prevent complications.
Q: What are the usually used methods that help control Crohn’s?
A: The treatment line includes two groups of medicines (anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system modifiers, antibiotics, and anti-diarrheal medicines), nutritional intervention, and surgery if the problem becomes severe.
Q: A diet can be an effective means of managing Crohn’s disease.
A: Let me tell that dieticians will be of help in creating the diet plan which will help to control the symptoms, support your body for healing, and enable to intake all the required nutrients. Some aspects of dietary changes like avoiding trigger foods, increase the portion of fiber in the diet, and diversification of nutrients intake may be included there.
Q: Is life threatening? Does a Crohn’s Disease exist?
A: Individuals who have Crohn’s Disease must know that the condition isn’t usually a life-threatening one with adequate treatment and control by their doctors. It also can become very dangerous if not treated at the initial stages and when other complexities like obstruction or severe malnutrition occur.
Q: Does Crohn’s Disease deterioration, or the onset of symptoms, depend on stress?
A: Yes, there is a strong correlation between the stress situation and the severity of the Crohn’s Disease flare-ups in patients. The coping with stress by using means such as relaxation methods, counseling, or support groups is what is most important to an individual who suffers from Crohn’s Disease.
Q: Can either female or male Crohn’s suffer any fertility or fetus burden during pregnancy?
A: Crohn’s disease could strike fertility in both male and female and further extra monitoring and care could be needed before, during and after the pregnancy to make sure that the condition is managed and all the two (2) of the mother and the baby stays safe and healthy.